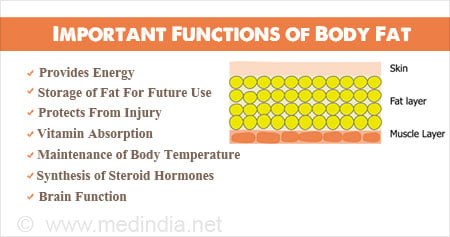
The Vital Role of Dietary Fats in Providing Energy to the Body
Dietary fats, often misunderstood and maligned, are an essential component of a well-balanced diet. While carbohydrates are known for their immediate energy-providing capabilities, fats play a distinct and equally important role in providing energy to the body. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricate mechanisms through which dietary fats contribute to energy production, their storage, and their impact on overall health.
Understanding Dietary Fats
Dietary fats, also known as lipids, are a diverse group of organic molecules that include triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols. Among these, triglycerides are the most common and well-known type of dietary fat. Triglycerides consist of three fatty acid molecules attached to a glycerol backbone. The length and saturation of fatty acids determine the characteristics of dietary fats and how they are metabolized in the body.
Energy Density of Dietary Fats
One of the key attributes of dietary fats is their high energy density. Fats provide more than twice the energy per gram compared to carbohydrates and proteins. While carbohydrates and proteins provide 4 calories per gram, fats provide a concentrated 9 calories per gram. This high energy density makes fats a potent source of sustained energy storage in the body.
Energy Storage: A Fuel Reserve
Dietary fats serve as an efficient energy storage system for the body. When you consume more calories than your body needs, the excess energy from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is converted into triglycerides and stored in specialized fat cells called adipocytes. These adipocytes accumulate in adipose tissue located under the skin and around organs, serving as a readily available energy reserve.
Metabolism of Dietary Fats for Energy
The breakdown of dietary fats for energy involves a series of complex processes. When energy is required, stored triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol in a process called lipolysis. Fatty acids are then released into the bloodstream and transported to cells throughout the body.
Once inside the cell, fatty acids can undergo β-oxidation, a metabolic pathway that takes place in the mitochondria. This process involves breaking down fatty acids into smaller units, which are then converted into acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA molecules enter the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) and the electron transport chain, generating ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. This energy production pathway is highly efficient and provides a sustained source of energy, particularly during activities that require endurance and prolonged effort.
Role in Sustained Energy and Endurance
Dietary fats play a critical role in providing sustained energy, especially during activities that require endurance, such as long-distance running or extended periods of physical exertion. While carbohydrates are readily available for immediate energy, fats are the body’s go-to source when activities continue beyond the initial burst of energy provided by carbohydrates. Fat metabolism is crucial in sparing glucose (derived from carbohydrates) for the brain and other essential functions during prolonged physical activity.
Essential Fatty Acids and Health
In addition to providing energy, dietary fats are the source of essential fatty acids—omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids—that the body cannot produce on its own. These fatty acids play crucial roles in maintaining cell structure, supporting immune function, regulating inflammation, and contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Balancing Fat Intake
While dietary fats are essential, it’s important to emphasize that not all fats are created equal. Consuming a diet high in unhealthy trans fats and saturated fats can contribute to health issues such as heart disease and obesity. On the other hand, incorporating healthy unsaturated fats—found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish—can provide the energy needed while offering additional health benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dietary fats are a fundamental source of energy that the body relies on for various physiological processes. Their high energy density, role in energy storage, and contribution to sustained endurance activities highlight their significance in maintaining overall health and vitality. Striking a balance between different types of fats and incorporating them into a balanced diet ensures that the body has the necessary resources to function optimally and perform at its best. Recognizing the crucial role of dietary fats sheds light on their importance as a cornerstone of human nutrition and well-being.



