Arteries vs. Veins: Unraveling the Key Differences in the Circulatory System
The circulatory system is an intricate network of blood vessels that facilitates the transportation of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. At its core, this system comprises two primary types of blood vessels: arteries and veins. While both are integral to the circulation of blood, they exhibit distinct characteristics and serve different functions. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the differences between arteries and veins, shedding light on their structure, function, and vital roles within the circulatory system.
Arteries: Paving the Way for Oxygen-Rich Blood
Arteries are vessels that carry blood away from the heart, making them a crucial component of the circulatory system’s outbound pathway. Here are the key characteristics that distinguish arteries from veins:
1. Blood Flow Direction
The most fundamental difference between arteries and veins lies in the direction of blood flow. Arteries transport oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to various parts of the body, ensuring that vital organs and tissues receive the oxygen and nutrients they need to function optimally.
2. Oxygen Content
Arterial blood is oxygenated, meaning it carries a high concentration of oxygen. This oxygen-rich blood is pumped by the left ventricle of the heart into the aorta, the largest artery in the body, which then branches into smaller arteries that distribute blood to different regions.
3. Wall Thickness and Elasticity
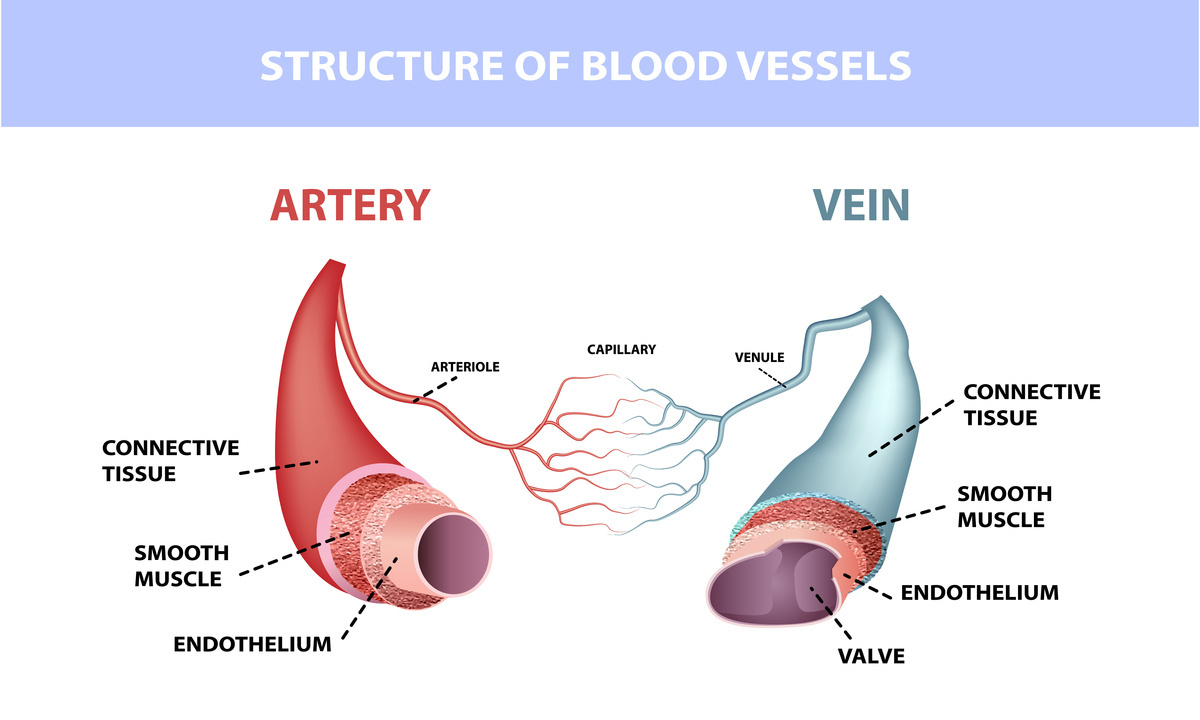
Arteries have thick, muscular walls designed to withstand the high-pressure environment generated by the heart’s forceful contractions. These walls are elastic, allowing arteries to expand and contract with each heartbeat, maintaining steady blood flow and pressure.
4. Pulse
The elasticity of arterial walls results in a characteristic pulse that can be felt at various pulse points throughout the body. Monitoring the pulse rate and rhythm is a vital diagnostic tool in healthcare.
5. Oxygen Reserve
Arteries do not have a significant oxygen reserve; their primary function is to transport oxygen to tissues. This is in contrast to veins, which store a larger portion of the body’s blood volume.
Veins: The Return Journey for Deoxygenated Blood
Veins, the counterparts of arteries in the circulatory system, play a critical role in returning deoxygenated blood from the body’s tissues back to the heart. Here are the key attributes that set veins apart:
1. Blood Flow Direction
Veins transport deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body back to the heart, specifically to the right atrium. This blood is low in oxygen and has already delivered nutrients to the body’s cells.
2. Wall Thickness and Elasticity
Compared to arteries, veins have thinner walls with less muscle tissue. This is because veins operate under lower pressure, as blood has already been distributed to the body’s tissues and does not need to withstand the force of the heart’s contractions.
3. Valves
Veins contain one-way valves that prevent the backward flow of blood. These valves are particularly important in the extremities, such as the legs, where they help counteract the effects of gravity and facilitate the return of blood to the heart.
4. Blood Volume Reserve
Unlike arteries, veins serve as blood reservoirs, storing a significant portion of the body’s blood volume. This stored blood can be quickly mobilized and directed to areas with increased demand, such as during physical activity.
Conclusion
Arteries and veins, while both integral to the circulatory system, have distinct roles and characteristics. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, have thick muscular walls, and exhibit elasticity, which allows them to withstand high pressure and maintain a steady blood flow. In contrast, veins transport deoxygenated blood back to the heart, have thinner walls with valves to prevent backflow, and serve as blood reservoirs.
Understanding the differences between arteries and veins is crucial in the field of medicine, as it aids in diagnosing and treating various cardiovascular conditions. Moreover, this knowledge highlights the remarkable complexity and precision of the circulatory system, a vital network that sustains life by ensuring the efficient distribution of oxygen, nutrients, and metabolic waste products throughout the human body.



