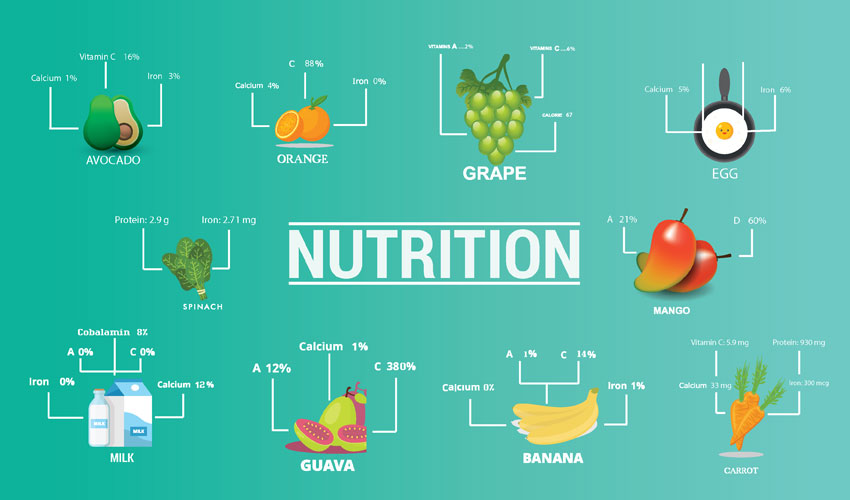
Exploring the Essential Types of Nutritions: A Comprehensive Guide
Nutrition is the cornerstone of human health and well-being. It provides the body with the necessary elements to function, grow, repair, and thrive. The foods we consume contain a diverse array of nutrients, each playing a unique role in supporting various bodily functions. Understanding the different types of nutrients is crucial for making informed dietary choices and ensuring optimal health. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the essential types of nutrients, their functions, sources, and their impact on the human body.
1. Carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are divided into two main categories:
a. Simple Carbohydrates:
These are quickly digested sugars found in foods such as fruits, honey, and processed sugars. They provide rapid energy but can lead to energy crashes and spikes in blood sugar levels if consumed excessively.
b. Complex Carbohydrates:
Complex carbohydrates, found in foods like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, are composed of longer chains of sugars. They release energy gradually, providing sustained fuel for the body. They also contain fiber, aiding in digestion and promoting a feeling of fullness.
2. Proteins:
Proteins are essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. They are composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks of life. There are two types of proteins:
a. Complete Proteins:
Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. Sources include animal products like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy.
b. Incomplete Proteins:
Incomplete proteins lack one or more essential amino acids. They are commonly found in plant-based sources such as beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds. Combining different incomplete protein sources can create a complete protein profile.
3. Fats:
Dietary fats play a vital role in energy storage, insulation, and protection of organs. There are three main types of dietary fats:
a. Saturated Fats:
These are primarily found in animal products and some plant oils. Excessive consumption of saturated fats is linked to an increased risk of heart disease and high cholesterol levels.
b. Unsaturated Fats:
Unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are considered healthier options. They can be found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and oily fish. These fats support heart health and reduce inflammation.
c. Trans Fats:
Trans fats are artificially produced fats often found in processed and fried foods. They are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and should be minimized in the diet.
4. Vitamins:
Vitamins are organic compounds that facilitate various biochemical reactions in the body. They are classified into two categories:
a. Water-Soluble Vitamins:
These vitamins (e.g., vitamin C, B vitamins) are not stored in the body and must be consumed regularly. They play roles in energy production, immune function, and more.
b. Fat-Soluble Vitamins:
Vitamins A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble and are stored in the body’s fatty tissues. They are essential for functions such as vision, bone health, and blood clotting.
5. Minerals:
Minerals are inorganic elements necessary for diverse physiological functions. They are divided into two groups:
a. Major Minerals:
These include calcium, magnesium, sodium, and potassium. They are needed in relatively larger amounts and are crucial for maintaining proper fluid balance, nerve function, and bone health.
b. Trace Minerals:
Trace minerals, such as iron, zinc, selenium, and copper, are required in smaller quantities. Despite their lower amounts, they are equally important for functions like oxygen transport, immune support, and enzyme activation.
6. Water:
Water is often overlooked as a nutrient, but it is essential for life. It facilitates chemical reactions, transports nutrients, regulates body temperature, and supports various bodily functions. Staying adequately hydrated is crucial for overall health.
Conclusion:
A balanced diet that includes a variety of foods rich in these essential nutrients is key to maintaining optimal health. Each type of nutrient plays a unique role in supporting various bodily functions, from energy production to immune support. By understanding the different types of nutrients and their sources, we can make informed choices that promote well-being and longevity. Remember, a holistic approach to nutrition is not just about consuming nutrients but also about enjoying a diverse and well-rounded diet.



