The olfactory sense organ, commonly known as the nose, is an intricate and remarkable part of the human body’s sensory system. It serves as the primary gateway to one of our most primal and powerful senses: the sense of smell. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the anatomy and physiology of the olfactory system, its primary functions, its incredible sensitivity, its role in daily life, and its broader significance in human evolution and health.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Olfactory System
The olfactory system is a complex network of structures responsible for detecting and processing odors. It includes the following key components:
1. Olfactory Epithelium
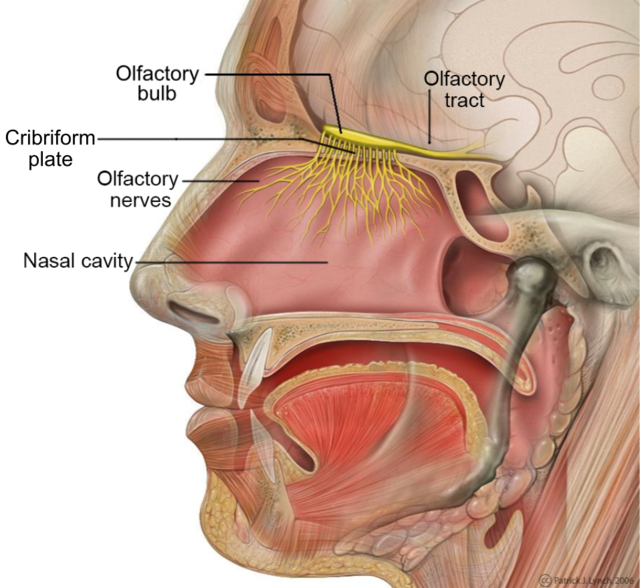
Located high in the nasal cavity, the olfactory epithelium contains millions of olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs). These specialized nerve cells have hair-like structures called cilia that extend into the nasal mucus.
2. Olfactory Bulb
The olfactory bulb is a structure at the base of the brain that receives signals from the ORNs. It processes and relays these signals to other brain regions for further interpretation.
3. Olfactory Cortex
The olfactory cortex, which includes areas like the piriform cortex and the orbitofrontal cortex, is responsible for the perception of smell and the emotional and memory-related aspects of odor.
4. Limbic System
The olfactory system is closely connected to the limbic system, a group of brain structures involved in emotions, memory, and behavior. This connection explains why smells can trigger vivid memories and strong emotional responses.
The Primary Function: Sensing Odors
The primary and most fundamental function of the olfactory sense organ is to detect and identify odors. This sensory ability is crucial for several reasons:
1. Warning of Danger
The sense of smell can alert us to potentially hazardous situations. For example, the smell of smoke can indicate a fire, and the scent of spoiled food can prevent foodborne illnesses.
2. Enjoyment of Food
The olfactory system plays a pivotal role in the flavor of food. It allows us to discern the nuanced tastes and aromas in various dishes, enhancing the overall dining experience.
3. Social and Sexual Attraction
Odors play a substantial role in social interactions and mate selection. People are often attracted to others based on their natural body odor, which can indicate compatibility and genetic diversity.
4. Memory and Emotion
The olfactory system has a strong connection to memory and emotion. Certain smells can evoke powerful memories and feelings, often more vividly than other sensory stimuli.
5. Environmental Navigation
In animals, including humans, the sense of smell can aid in navigation. This is particularly evident in animals like homing pigeons, which rely on their olfactory senses to find their way home.
Incredible Sensitivity
The olfactory system is exceptionally sensitive. Humans can detect an extensive range of odors, often in minuscule quantities. Some estimates suggest that humans can distinguish between thousands of different odors, showcasing the system’s remarkable discriminatory abilities.
Olfaction in Evolution and Health
The sense of smell has deep evolutionary roots. It likely originated as a means for early organisms to detect food, predators, and environmental changes. Over time, it became more refined, contributing to the survival and development of various species.
From a health perspective, the olfactory sense organ is also vital. Loss of the sense of smell, known as anosmia, can be a symptom of various medical conditions, including infections, neurological disorders, and head injuries. Anosmia can have profound effects on a person’s quality of life, affecting their ability to enjoy food, detect danger, and experience the world fully.
Conclusion
The olfactory sense organ is an extraordinary and underappreciated part of the human body. Its primary function, detecting and identifying odors, has profound implications for our safety, enjoyment of life, social interactions, and memory. Its incredible sensitivity and its evolutionary significance underscore its critical role in the human experience. Understanding the olfactory system’s complexities not only deepens our appreciation for this sense but also highlights its importance in our daily lives and in the broader context of human evolution and health.



