The lymphatic system is often overshadowed by its more famous counterpart, the circulatory system, which consists of the heart and blood vessels. However, this lesser-known system plays an equally vital role in maintaining the health and function of the human body. The primary function of the lymphatic system is to serve as a key component of the immune system and to facilitate the circulation of lymph, a colorless fluid that helps defend the body against infections, maintain fluid balance, and support overall health.
Understanding the Lymphatic System
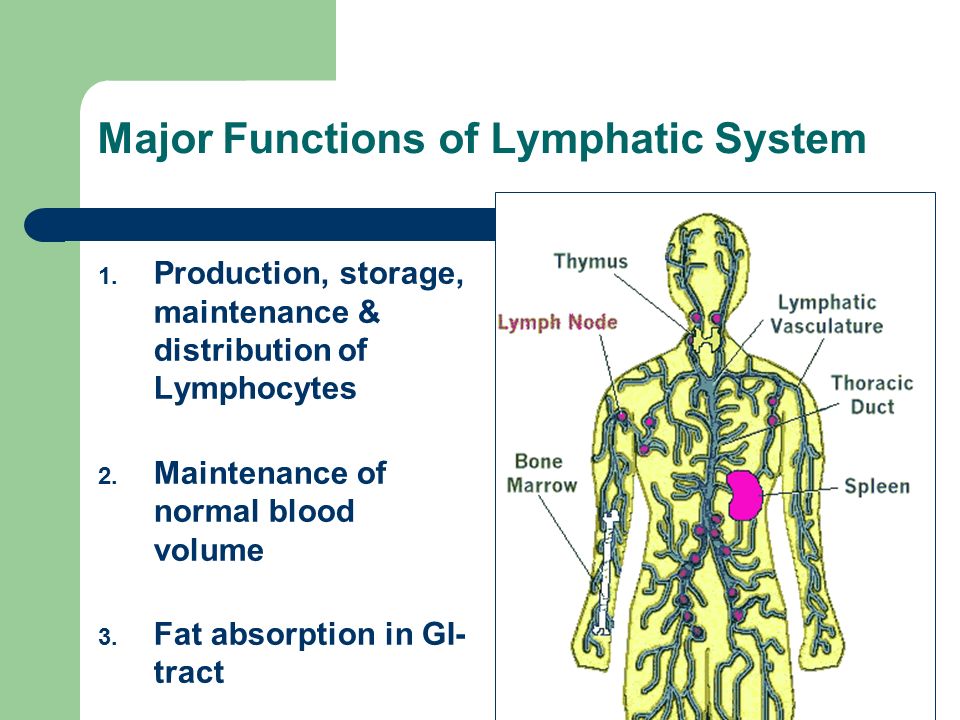
Before delving into its primary function, let’s explore the lymphatic system’s anatomy and components. The lymphatic system is a complex network of vessels, organs, and tissues that work together to transport lymph throughout the body. It includes:
1. Lymphatic Vessels
Lymphatic vessels, similar in structure to blood vessels, are responsible for carrying lymph throughout the body. They have thin walls and contain one-way valves that prevent the backward flow of lymph.
2. Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures strategically located throughout the lymphatic system. They act as filters, trapping and removing foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses, from the lymph before it re-enters the bloodstream.
3. Tonsils and Adenoids
Tonsils and adenoids are specialized lymphatic tissues located in the throat. They help defend against inhaled or ingested pathogens and play a role in immune responses.
4. Spleen
The spleen is the largest lymphatic organ in the body. It filters blood, removing damaged blood cells and pathogens, and stores platelets and white blood cells for immune responses.
5. Thymus
The thymus is responsible for the maturation of T lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell crucial for cell-mediated immunity.
6. Bone Marrow
Bone marrow, a spongy tissue within bones, is the site of blood cell production, including lymphocytes (white blood cells).
The Primary Function of the Lymphatic System
The primary function of the lymphatic system is to support the immune system and maintain fluid balance within the body:
1. Immune System Support
The lymphatic system plays a central role in immune defense. Lymph contains white blood cells, primarily lymphocytes, which are essential for immune responses. When the body encounters pathogens (harmful microorganisms), such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, lymphocytes are activated to mount an immune response. Lymphocytes identify and target these invaders, helping the body defend itself against infections.
2. Pathogen Removal
Lymph nodes are critical for filtering out and trapping pathogens and foreign substances from the lymph. When pathogens are detected, lymph nodes produce additional immune cells and antibodies to fight off the infection. Swollen or tender lymph nodes often indicate an active immune response.
3. Fluid Balance
The lymphatic system also plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance. Excess fluid from the body’s tissues, called lymphatic fluid or lymph, is collected by lymphatic vessels. This fluid contains waste products, cellular debris, and proteins that have leaked from blood vessels. The lymphatic system returns this fluid to the bloodstream, helping to prevent tissue swelling (edema).
4. Fat Absorption
Another important but less-known function of the lymphatic system is the absorption of dietary fats. In the small intestine, lymphatic vessels called lacteals absorb dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins, transporting them to the bloodstream for distribution to cells throughout the body.
Conclusion
The lymphatic system’s primary function is to support the immune system and maintain fluid balance in the body. This intricate network of vessels, nodes, and organs acts as a surveillance system, helping to identify and eliminate pathogens while also preventing tissue swelling and assisting in dietary fat absorption. Understanding the crucial role of the lymphatic system underscores its significance in overall health and underscores the intricate interplay between different systems within the human body.




