How Many Types of Muscles Are There in the Human Body?
Muscles are a fundamental component of the human body, enabling movement, supporting posture, and facilitating vital functions. While we often associate muscles with activities like lifting weights or running, there is a remarkable diversity in the types of muscles found throughout the body. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the different types of muscles in the human body, their structure, functions, and how they contribute to our overall health and well-being.
Types of Muscles
Muscles in the human body can be broadly categorized into three main types based on their structure, location, and function:
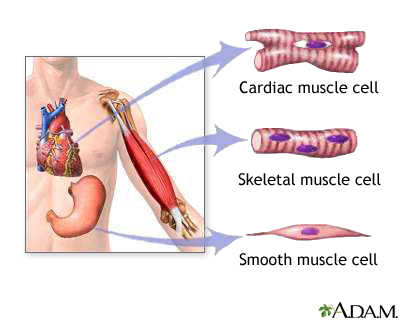
1. Skeletal Muscles: Powerhouses of Movement
Skeletal muscles are the most familiar type of muscles and are often what people think of when they hear the term “muscles.” They are attached to bones by tendons and are responsible for voluntary movements such as walking, running, and lifting objects. Skeletal muscles are under conscious control and work in pairs, with one muscle contracting to move a joint while the other relaxes.
Structure: Skeletal muscles are composed of long, cylindrical muscle fibers that contain multiple nuclei. These fibers are bundled together to form muscle fascicles, which, in turn, make up the entire muscle.
Function: Skeletal muscles provide the force required for body movement, maintain posture, and generate heat. They are essential for activities of daily living and are the muscles you train during exercise.
2. Smooth Muscles: Invisible Workhorses
Smooth muscles, also known as involuntary or visceral muscles, are found in the walls of internal organs and structures such as the digestive tract, blood vessels, and respiratory passages. Unlike skeletal muscles, they are not under conscious control and work involuntarily.
Structure: Smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped and lack the striated appearance seen in skeletal muscles. They have a single nucleus and are connected by gap junctions, allowing them to contract as a unit.
Function: Smooth muscles regulate various bodily functions, including the movement of food through the digestive tract (peristalsis), the constriction and dilation of blood vessels, and the control of airflow in the lungs. They also play a role in maintaining blood pressure and organ function.
3. Cardiac Muscle: The Heart’s Rhythmic Beat
Cardiac muscle is a specialized type of muscle found exclusively in the heart. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, ensuring the circulation of oxygen and nutrients to tissues.
Structure: Cardiac muscle cells are striated like skeletal muscle but are smaller and branched. They are connected by intercalated discs, which allow for coordinated contractions. Cardiac muscle cells each contain a single nucleus.
Function: The rhythmic and coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle propel blood through the heart chambers and into the circulatory system. Unlike skeletal muscles, cardiac muscle contracts involuntarily and continuously throughout life.
Unique Characteristics and Significance
Each type of muscle in the human body has unique characteristics and plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and function:
- Voluntary vs. Involuntary Control: Skeletal muscles are under voluntary control, allowing us to consciously move our bodies. In contrast, smooth and cardiac muscles operate involuntarily, ensuring the functioning of internal processes without conscious effort.
- Striated vs. Non-Striated: Skeletal and cardiac muscles are striated due to their organized sarcomere structure, while smooth muscles lack this striated appearance.
- Continuous Contraction: Cardiac muscle contracts continuously to pump blood, and it does so throughout a person’s life without fatiguing.
- Maintenance of Vital Functions: All three types of muscles contribute to the maintenance of vital functions such as circulation, digestion, and respiration.
Importance of Muscle Health
Maintaining healthy muscles is essential for overall well-being. Muscles not only enable mobility and physical activity but also influence metabolic health, posture, and body composition. Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate rest are crucial for preserving muscle health and function.
In conclusion, the human body possesses three distinct types of muscles, each with its own structure, function, and significance. Skeletal muscles enable voluntary movement, smooth muscles control internal processes, and cardiac muscles keep our hearts beating rhythmically. Understanding the diversity and roles of these muscles underscores their importance in our daily lives and highlights the need for proper care to ensure a healthy and functional musculoskeletal system.



