Explaining the Difference Between Simple Carbohydrates and Complex Carbohydrates: Examples Included
Carbohydrates are a crucial component of our diet, providing energy and playing various roles in maintaining our health. Carbohydrates can be classified into two main categories: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Understanding the differences between these two types of carbohydrates is essential for making informed dietary choices. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the distinctions between simple and complex carbohydrates, providing examples to illustrate each category’s characteristics.
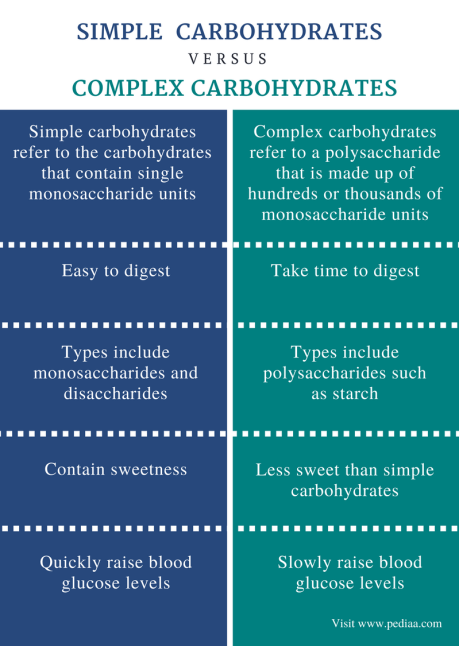
Simple Carbohydrates: The Quick Energy Boosters
Simple carbohydrates, often referred to as “simple sugars,” consist of one or two sugar molecules. Due to their simple chemical structure, they are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. This quick energy boost is followed by a crash, often leaving individuals feeling hungry shortly after consumption. Simple carbohydrates are commonly found in sugary and processed foods, making them a less nutritious choice compared to complex carbohydrates.
Examples of Simple Carbohydrates:
- Glucose: Glucose is a monosaccharide that serves as a primary source of energy for the body. It is found in foods like honey and fruits.
- Fructose: Another monosaccharide, fructose, is naturally present in fruits and honey. It is also used as a sweetener in many processed foods and beverages.
- Sucrose: Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose. It is commonly known as table sugar and is often used to sweeten foods and beverages.
- Lactose: Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk and dairy products. It consists of glucose and galactose.
- Added Sugars: Sugars added to foods during processing, such as high fructose corn syrup, are also considered simple carbohydrates. These are commonly found in candies, soft drinks, and baked goods.
Complex Carbohydrates: Sustained Energy Providers
Complex carbohydrates, as the name suggests, are more intricate in structure. They consist of multiple sugar molecules linked together in longer chains, making them take longer to break down during digestion. This slower digestion results in a gradual and more sustained release of glucose into the bloodstream, providing a steady source of energy over time. Complex carbohydrates are found in whole foods that are generally richer in nutrients and dietary fiber.
Examples of Complex Carbohydrates:
- Starch: Starch is a complex carbohydrate found in plant-based foods such as grains (e.g., rice, wheat, oats), legumes (e.g., beans, lentils), and starchy vegetables (e.g., potatoes, corn). It serves as a primary energy storage form in plants.
- Dietary Fiber: Dietary fiber, also a type of complex carbohydrate, is found in plant foods and is not fully digestible by human enzymes. It includes soluble fiber, which can help lower cholesterol levels, and insoluble fiber, which aids in promoting healthy digestion. Examples include vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and seeds.
- Glycogen: While also a complex carbohydrate, glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals, primarily in the liver and muscles. It serves as a readily available energy source during times of increased demand, such as physical activity.
Choosing Wisely: Balancing Simple and Complex Carbohydrates
When considering the nutritional value of carbohydrates, it’s important to make thoughtful choices:
- Simple carbohydrates: While they can provide quick bursts of energy, it’s best to limit consumption of foods high in added sugars. Instead, opt for natural sources of simple sugars like fruits, which also provide vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
- Complex carbohydrates: Foods rich in complex carbohydrates offer sustained energy and additional nutrients. Choose whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits to ensure a balanced and nutritious diet.
Conclusion
The distinction between simple and complex carbohydrates lies in their chemical structure and how they affect our bodies’ energy levels. Simple carbohydrates provide rapid energy but lack essential nutrients and can lead to energy crashes. Complex carbohydrates offer sustained energy and are accompanied by valuable nutrients and dietary fiber. By understanding the differences between these two carbohydrate categories and making mindful dietary choices, individuals can optimize their energy levels, overall health, and well-being.



